Electrospinning is a new and innovative low cost process that allows the easy and fast deposition of nanostructured materials onto any surface. In the process of electrospinning, the applied voltage causes a cone-shaped deformation of the drop of polymer solution (Taylor cone – figure 1). The electrified jet elongates and moved towards the collector, the solvent evaporates, inducing the formation of nonwoven nanostructured dense web of nanofibers (figure 2). Nanofibers can be prepared from various polymers, blends, composites, ceramics, etc. Co-axial electrospinning offers the possibility to produce core-shell nanofibers using a co-axial emitter (figure 3). These consist of an inner and outer layer, which can be tailored for a wide range of applications and their needs.
Spraybase® Electrospinning device – Specifications:
- Power voltage supply (0-20 kV). Current: 0.5 mA
- Syringe pump to deliver solution to the emitter tip
- Software controlled flow rate
- Flow rate of 0.75 μl/hr to a maximum 2100 ml/hr
- Maximum syringe size is 60 ml
- Taylor cone visualization system
- Flat Plate Collector – collection area: 145x230x1 mm
- Single emitter
- Co-axial emitter
- Z positioning system: distance between emitter and collector up to 22 cm
- Z-Positioniersystem: Abstand zwischen Sender und Kollektor bis zu 22 cm
Nanofibers applications:
- Filtration
- Energy devices (fuel cells, batteries, solar cells, supercapacitors, hydrogen production/ storage)
- Sensors
- Corrosion protection
- Medical (tissue engineering, wound healing, regenerative medicine, drug delivery, scaffolds)
- Textiles
- Food science
- Composites
- Encapsulation

Figure 1: Taylor cone
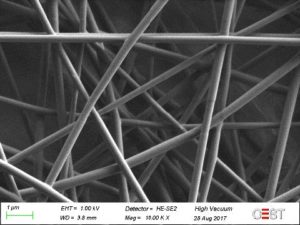
Figure 2: Electrospun nanofibers

Figure 3: Co-axial emitter

